In killing off Windows 10X, Microsoft might have just saved itself from a lot of trouble by not having to worry about app support and putting Windows 10 first.


In killing off Windows 10X, Microsoft might have just saved itself from a lot of trouble by not having to worry about app support and putting Windows 10 first.

Because of the ongoing pandemic, lifestyles have been subjected to drastic and dynamic changes, and many work- and study-related activities are now carried out online exclusively. This, among other complex factors, has made it difficult for some people to stay focused and motivated, and psychology researchers are trying to find effective and widely applicable solutions …
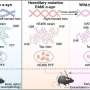
Amyloid deposition of α-synuclein (α-syn) is a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease (PD). α-Syn fibrillation and cell-to-cell transmission in the brain play an essential role in disease progression. To date, eight single-point mutations of SNCA have been identified in familial PD (fPD), which feature early-onset, severe and highly heterogeneous clinical symptoms.
Nurses traditionally manage insulin intake for critically ill patients by following precise steps to manually calculate the correct dose for each person. Looking for ways to improve this process, researchers at the Johns Hopkins Armstrong Institute for Patient Safety and Quality recently tested a “smart agent” system that integrates electronic health records and infusion pumps …

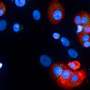
Adipose cells, better known as fat, may be the least popular component of the human body. However, most people don’t realize that fat actually has many important functions in establishing and maintaining good health—providing energy, insulating the body against heat loss and protecting nerves, just to name a few. Now, researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine …

Chronic itch—known clinically as chronic pruritus—is characterized as an unrelenting and sometimes even debilitating sensation to itch, and often lowers the quality of life for those who suffer with it. Treating the condition has been difficult because there are few Food and Drug Administration-approved therapies. Now, a recent case study by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers …

• What happened to the other 9 Republicans who voted to impeach Trump • Analysis: This one line from Cheney’s speech will haunt the GOP • Video: Cooper exposes GOP with side-by-side video

The Champions League final between Manchester City and Chelsea is to be played in Porto instead of Istanbul, European football’s governing body UEFA said on Thursday.
As bullets from a Taliban machine gun ricocheted through the street below, an Afghan soldier wearing an “I Heart Kabul” T-shirt took a brief rest. “There has been fighting day and night.”

President Joe Biden’s steadfast belief in taxing corporations and the rich has become a central plank in his legislative agenda, even as he’s warned of political peril and red lines from Republicans.