Scientists discover a new genetic form of ALS in children
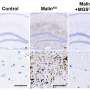
In a study of 11 medical-mystery patients, an international team of researchers led by scientists at the National Institutes of Health and the Uniformed Services University (USU) discovered a new and unique form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Unlike most cases of ALS, the disease began attacking these patients during childhood, worsened more slowly than usual, and was linked to a gene, called SPTLC1, that is part of the body’s fat production system. Preliminary results suggested that genetically silencing SPTLC1 activity would be an effective strategy for combating this type of ALS.