Serial antigen testing may be an effective strategy for controlling infection during a nursing home SARS-CoV-2 outbreak
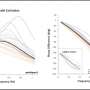
A prospective study found that serial antigen testing could be an effective strategy to support infection control in nursing homes having a SARS-CoV-2 outbreak. While less sensitive than real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) diagnostic tests, the authors say that antigen tests perform well when it counts—when someone is infectious and at risk for spreading the virus. The findings are published in Annals of Internal Medicine.